Validator System
Validator Operation
Comprehensive guide to validator lifecycle management, from creation to ongoing operations
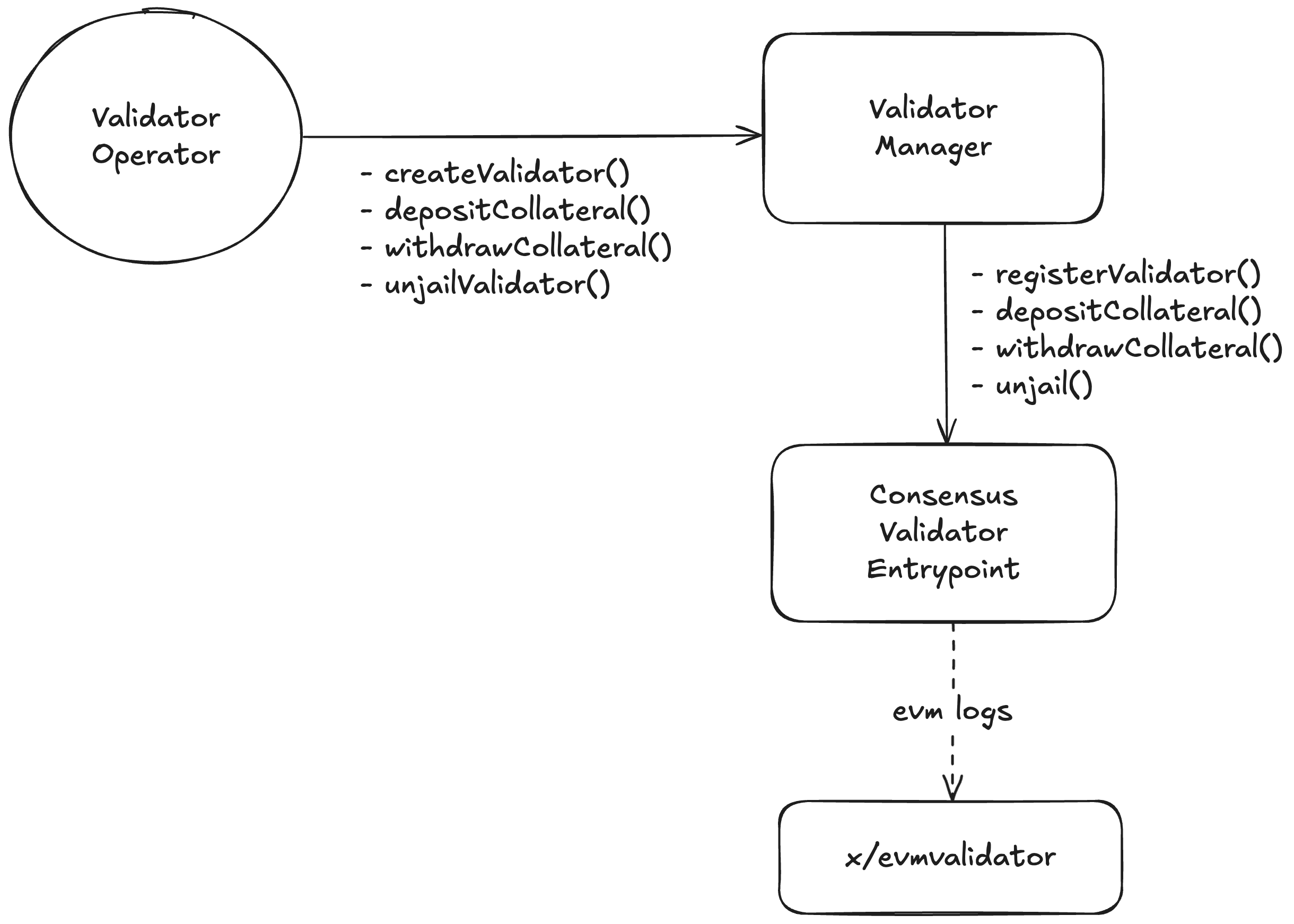 Mitosis validators are managed through the ValidatorManager contract, providing operators with complete control over validator lifecycle and configuration.
Mitosis validators are managed through the ValidatorManager contract, providing operators with complete control over validator lifecycle and configuration.
Professional Operation: Running a validator requires technical expertise, continuous monitoring, and commitment to network security. Consider the responsibilities carefully before becoming an operator.
Validator Lifecycle Overview
Create
Initial validator registration with consensus public key
Manage
Ongoing configuration and operational adjustments
Recover
Unjailing and troubleshooting procedures
Validator Creation
Prerequisites
Before creating a validator, ensure you have:- Node Setup Complete: Running Mitosis node with generated
priv_validator_key.jsonand fully synced to the latest block - Operator Wallet: EVM wallet for validator management transactions
- Initial Collateral: Minimum MITO tokens for validator creation
Creation Process
Mitosis provides the mito tool (available on GitHub) to streamline validator creation and management operations. This tool simplifies the entire process and handles key extraction and transaction submission automatically. For manual setup or understanding the underlying process, follow these steps: Step 1: Extract Consensus KeyscreateValidator() on the ValidatorManager contract:
Validator Management
Operators can modify validator settings through dedicated management functions:Update Operator Address
Update Reward Manager
Update Commission Rate
Commission Rate Delay Protection: To prevent abusing commission rate changes and protect stakers, updates are not applied immediately. Instead, they are scheduled to take effect after a delay period of several epochs (configured by
commissionRateUpdateDelayEpoch parameter).How it works:- Current commission rate continues to apply during the delay period
- New rate becomes effective at the scheduled future epoch
- Stakers can view pending rate changes and make decisions accordingly
Update Metadata
Collateral Management
For detailed information about collateral deposit, withdrawal, and ownership management, see Collateral Ownership.EVM-Only Operations: All configuration updates only affect EVM state and don’t require consensus layer interaction, enabling fast and gas-efficient management.
Validator Recovery
Understanding Jailing
Validators can be jailed by the consensus layer for various reasons:- Excessive Downtime: Missing too many consecutive blocks → Recoverable: Can be unjailed to resume consensus participation
- Double Signing: Conflicting block signatures (slashing event) → Permanent: Validator becomes tombstoned and can never be unjailed again
Unjailing Process
Step 1: Identify and Address Jail Reason- Node Process Issues: Restart crashed or stopped validator node
- Network Connectivity: Fix internet connection or firewall blocking P2P ports
- Disk Space: Free up disk space if node storage is full
- CPU/Memory: Upgrade hardware if node is resource-constrained
- Chain Upgrades: Update node binary if missed during network upgrade
Important: Jail status exists only on the consensus layer. A successful EVM transaction doesn’t guarantee consensus layer unjailing. Always verify unjailing success through consensus layer queries.

