Welcome
Introduction
Comprehensive technical overview of Mitosis for developers
Gmito, developers! 👋
This document provides a comprehensive technical overview of Mitosis and essential guides for developers.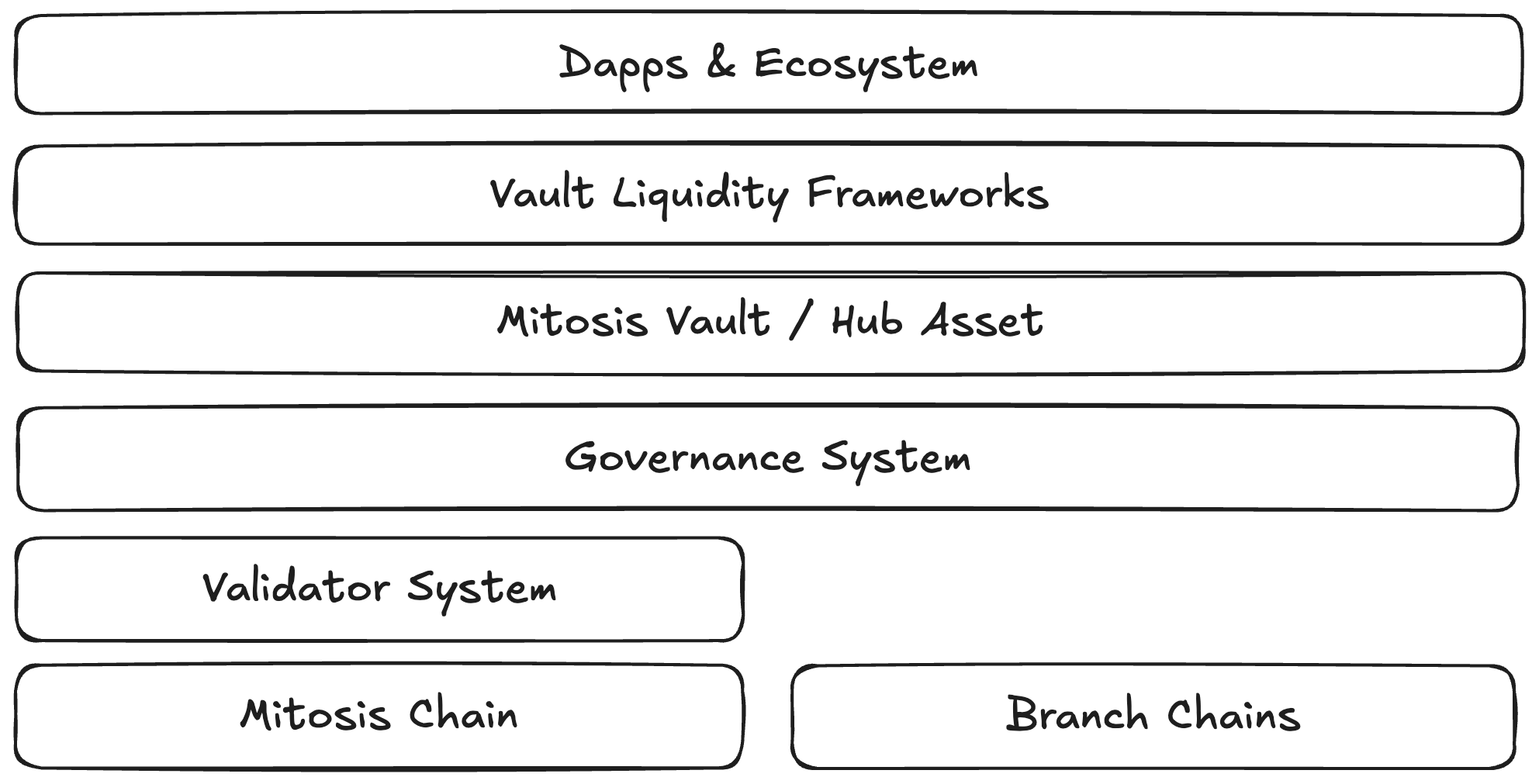
Key Technical Entities
From a technical perspective, the key entities in Mitosis can be categorized as follows:Mitosis Chain
- Mitosis Chain is a Layer 1 blockchain with an architecture that separates the Execution Layer and Consensus Layer based on the Engine API
- The Execution Layer provides a completely EVM-compatible execution environment
- The Consensus Layer is built on a Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism with instant finality and rapid block times, powered by CometBFT and Cosmos SDK
Branch Chains
- Branch chains are external blockchains where Mitosis Vaults are deployed and DeFi strategies are executed
- They form a hub-and-spoke architecture with Mitosis Chain as the central hub coordinating cross-chain operations
- Users deposit assets on branch chains, which are then represented as hub assets on Mitosis Chain
- VLF strategies operate on branch chains, accessing liquidity opportunities across diverse DeFi ecosystems
- Cross-chain messaging ensures secure coordination between branch chains and Mitosis Chain
Validator System
- Enables validator creation/management, staking, and reward distribution on the Mitosis Chain EVM
- Instead of using traditional Cosmos SDK modules like
x/stakingandx/distribution, we created our ownx/evmvalidatormodule to enable validator control on the consensus layer through the EVM
Governance System
- Provides governance functionality based on the gMITO (Mitosis Governance Token) on the Mitosis Chain EVM
- Through governance, users can control contracts across multiple layers: Mitosis Chain EVM, branch chains, and Consensus Layer modules
Mitosis Vault
- Users can deposit assets into the Mitosis Vault from supported chains and receive corresponding hub assets on the Mitosis Chain
- Hub assets are backed 1:1 by the underlying assets stored in the vault
Vault Liquidity Frameworks (VLFs)
- VLFs establish structured relationships between Mitosis LPs and DeFi protocols for liquidity opportunities
- They define reward accrual, distribution mechanisms, campaign duration, and lock-up requirements
- Representative examples include Matrix and EOL (Ecosystem-Owned Liquidity)
- VLF participation generates VLF assets such as mi/maAssets representing claims on underlying assets and generated yields
- Advanced settlement system handles yield, loss, and extra reward distribution
Dapps & Ecosystem
- Mitosis provides complete EVM compatibility, enabling developers to deploy existing Ethereum dApps instantly or create new ones using familiar Solidity tooling
- Developers can build innovative applications by leveraging core systems like Mitosis Vault and VLFs
Getting Started
Chain Architecture
Learn about Mitosis Chain’s modular architecture
Governance System
Understand the governance system and voting mechanisms
Validator System
Learn about validator operations, staking mechanisms, and network participation
Mitosis Vault
Discover how the Mitosis Vault enables secure cross-chain asset management
Vault Liquidity Frameworks
Understand VLFs for yield strategies and liquidity opportunities
Network Info
Access development environments and network specifications

